Motivation
- Previous region-based detectors such as Fast R-CNN and Faster R-CNN apply a costly per-region subnetwork hundreds of times
- Instead, use a fully convolutional network with almost computation shared on the entire image That is, from
feature_maps = process(image)
ROIs = region_proposal(feature_maps)
for ROI in ROIs
patch = roi_pooling(feature_maps, ROI)
class_scores, box = detector(patch)
class_probabilities = softmax(class_scores)
To
feature_maps = process(image)
ROIs = region_proposal(feature_maps)
score_maps = compute_score_map(feature_maps)
for ROI in ROIs
V = region_roi_pool(score_maps, ROI)
class_scores, box = average(V) # Much simpler!
class_probabilities = softmax(class_scores)
General Idea
If we need to detect the position of a human face, the traditional approach is to develop a feature map for this category. However, if we have other feature maps specialized in detecting the left eye, the nose or the mouth, we can combine information together to make face detection easier and more accurate.
To generalize this solution, we create 9 region-based feature maps each detecting the top-left, top-middle, top-right, middle-left, … or bottom-right area of an object. By combing the votes from these feature maps, we determine the class and the location of the objects.
Example
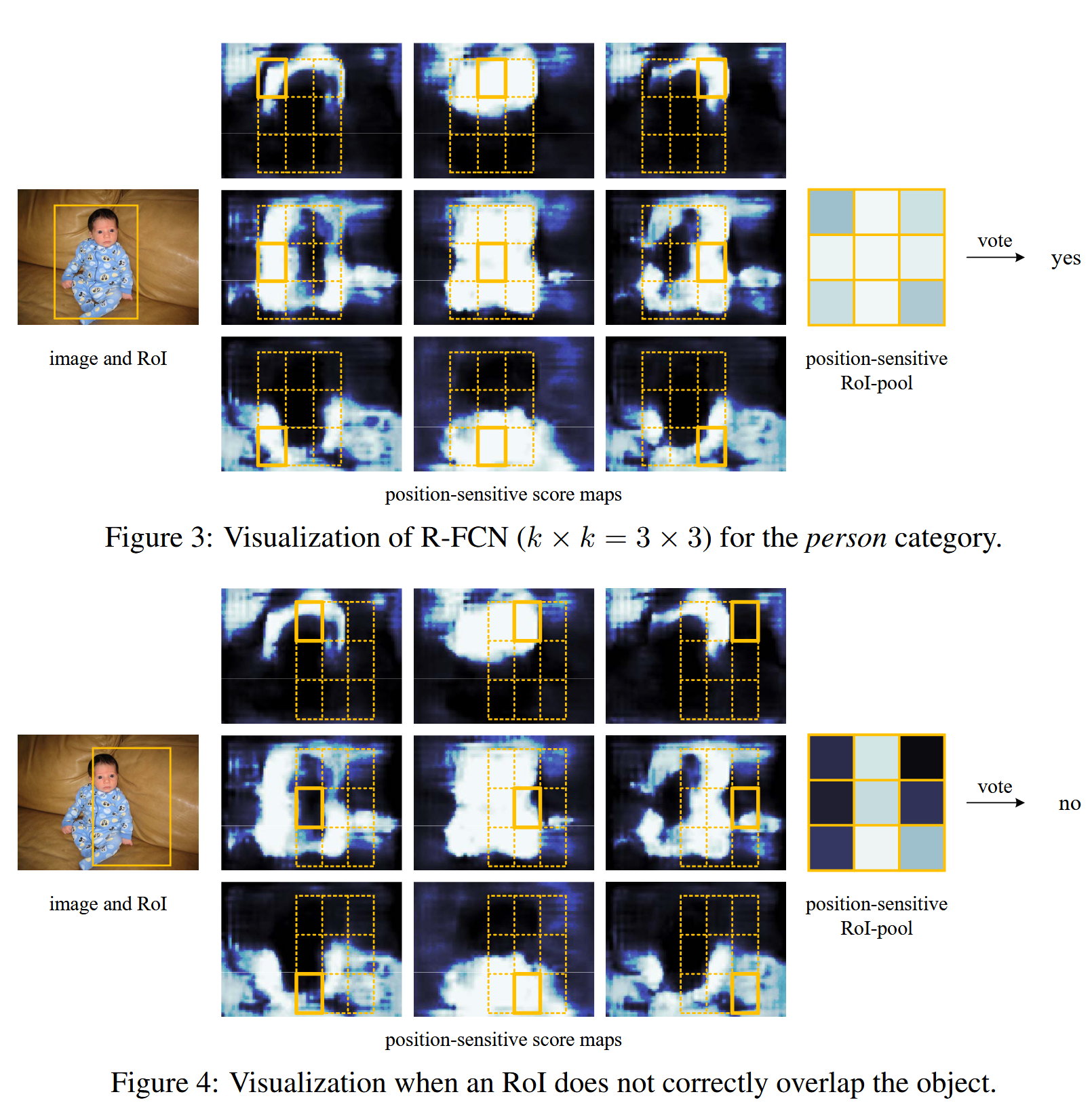
- For the whole input image, compute feature scores of each position ( in total, here ) of each class ( in total).
- Generate RoIs via a RPN
- Divide the RoI into regions, compute the scores for each region
- If the final vote is high, then this RoI is likely to be the region for the specific class
Architecture
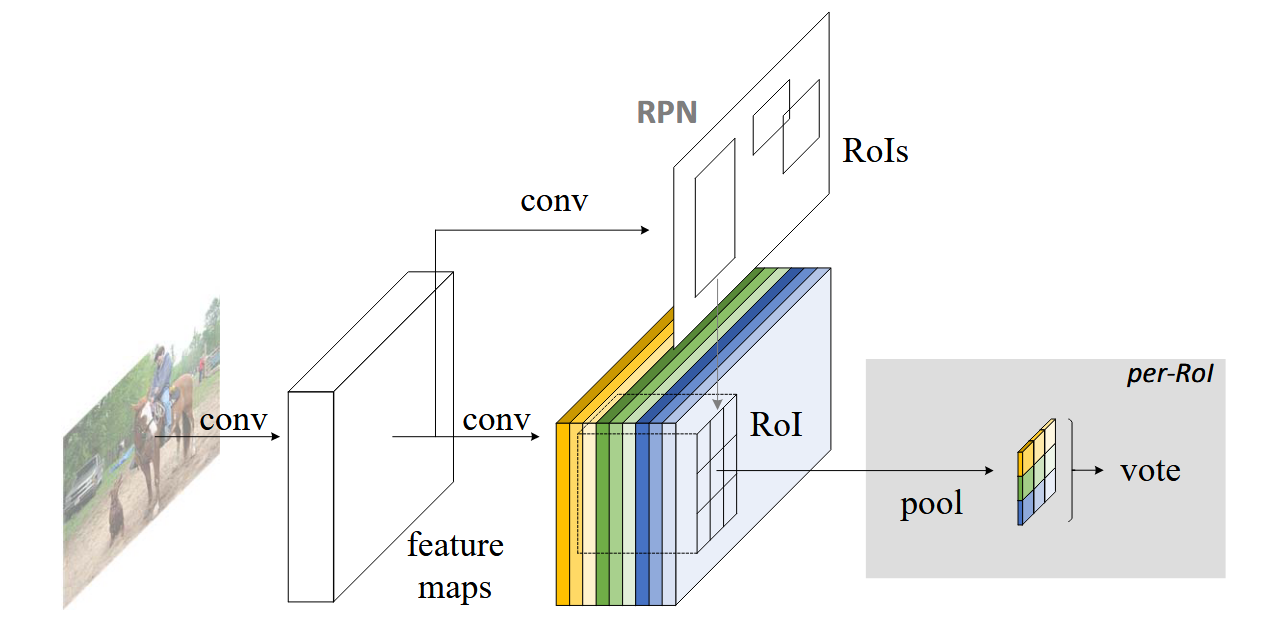
Overview
Adopt the popular two-stage object detection strategy that consists of
- Region proposal via RPN
- Region classification via R-FCN
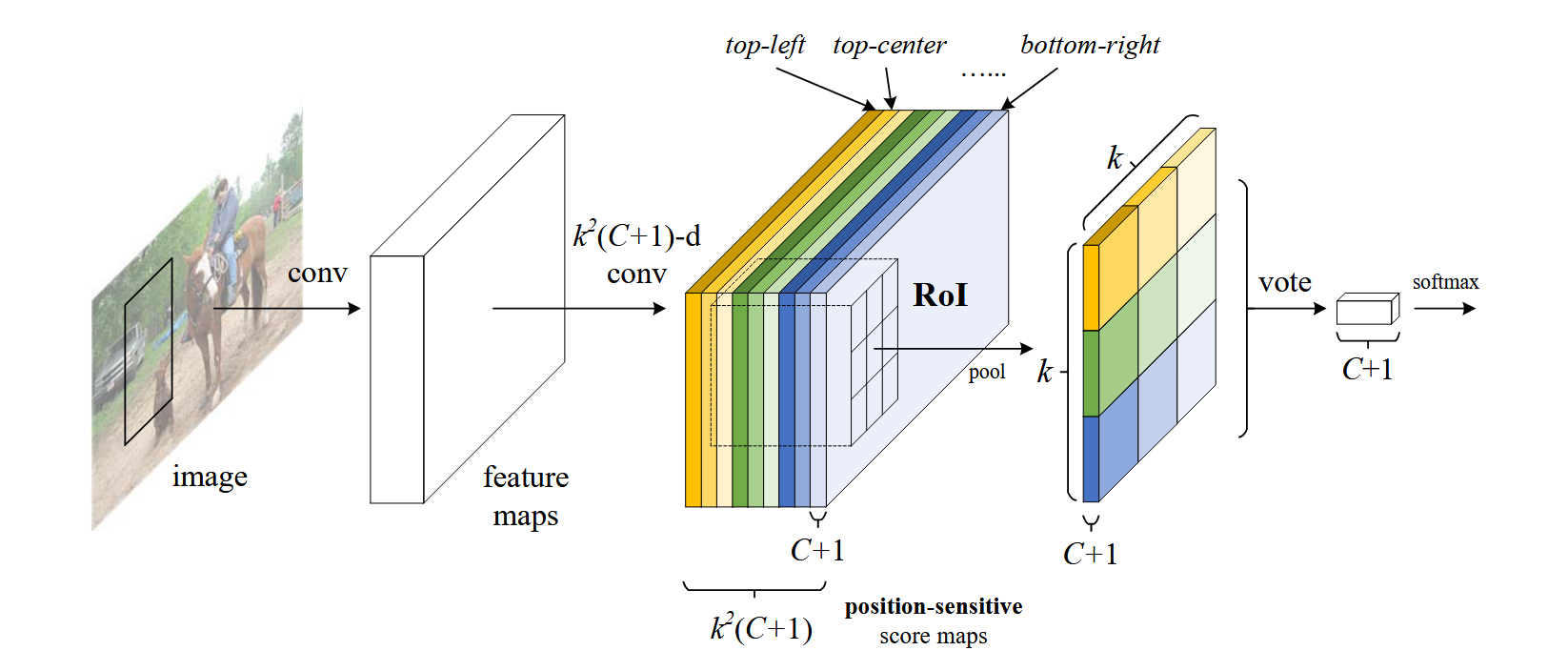
Given the proposal regions (RoIs), the R-FCN architecture is designed to classify the RoIs into object categories and background. In R-FCN, all learnable weight layers are convolutional and are computed on the entire image. The last convolutional layer produces a bank of position-sensitive score maps for each category, and thus has a -channel output layer with object categories ( for background).
The bank of score maps correspond to a spatial grid describing relative positions. For example, with , the score maps encode the cases of of an object category.
R-FCN ends with a position-sensitive RoI pooling layer. This layer aggregates the outputs of the last convolutional layer and generates scores for each RoI. The layer conducts selective pooling, and each of the bin aggregates responses from only one score map out of the bank of score map