Limitations of U-Net
By fusing the hierarchical features of the backbone network, the U-shape structure gradually increases the spatial resolution and fills some missing details. However, this technique has two weaknesses:
- The complete U-shape structure can reduce the speed of the model due to the introduction of extra computation on high-resolution feature maps.
- More importantly, most spatial information lost in the pruning or cropping cannot be easily recovered by involving the shallow layers. In other words, the U-shape technique is better to regard as a relief, rather than an essential solution.
Idea
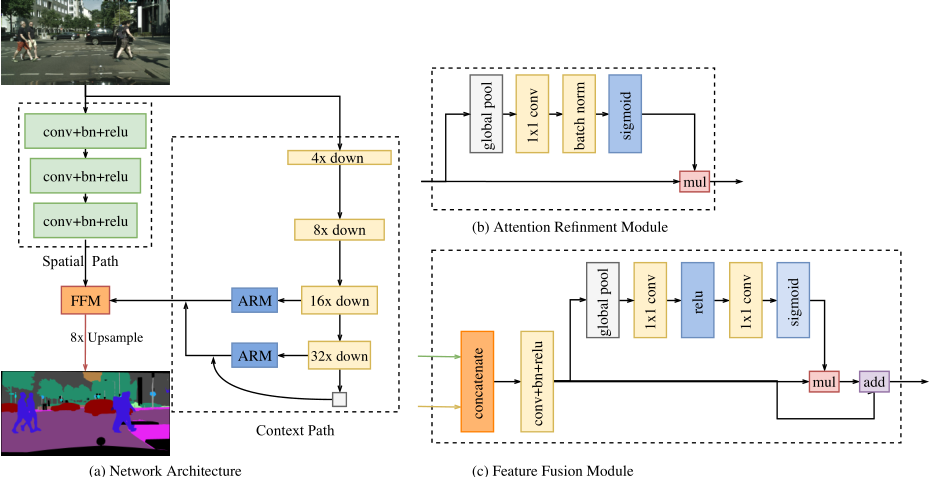
Split the forward process into two paths: Spatial Path and Context Path
- Spatial Path: stack only three convolution layers to obtain the feature map, which retains affluent spatial details. This path is designed to maintain more precise spatial information.
- Context Path: append a global average pooling layer on the tail of Xception (can be other backbone classification network like AlexNet and VGG), where the receptive field is the maximum of the backbone network. This path is designed to provide sufficient receptive field.
Architecture
 The key problem here is how to fuse the information from these two paths.
The key problem here is how to fuse the information from these two paths.
Attention Refinement Module (ARM)
ARM employs global average pooling to capture global context and computes an attention vector to guide the feature learning. This design can refine the output feature of each stage in the Context Path. It integrates the global context information easily without any up-sampling operation. Therefore, it demands negligible computation cost.
Feature Fusion Module (FFM)
The features of the two paths are different in level of feature representation.
- The spatial information captured by the Spatial Path encodes mostly rich detail information.
- The output feature of the Context Path mainly encodes context information. In other words, the output feature of Spatial Path is low level, while the output feature of Context Path is high level.
Given the different level of the features, we first concatenate the output features of Spatial Path and Context Path. And then we utilize the batch normalization to balance the scales of the features. Next, we pool the concatenated feature to a feature vector and compute a weight vector. This weight vector can re-weight the features, which amounts to feature selection and combination.