Idea
Assemble token from various stages of the vision transformer into image-like representations at various resolutions and progressively combine them into full-resolution predictions using a convolutional decoder
Transformer vs Convolutions
- Downsampling would lost feature resolution and granularity in deeper stages of the model and can thus be hard to recover in the decoder (May not matter for image classification, but are critical for dense prediction)
- Vision transformer foregoes explicit downsampling operations after an initial image embedding has been computed and maintains a representation with constant dimensionality throughout all processing stages
- The transformer has a global receptive field at every stage after the initial embedding.
Architecture
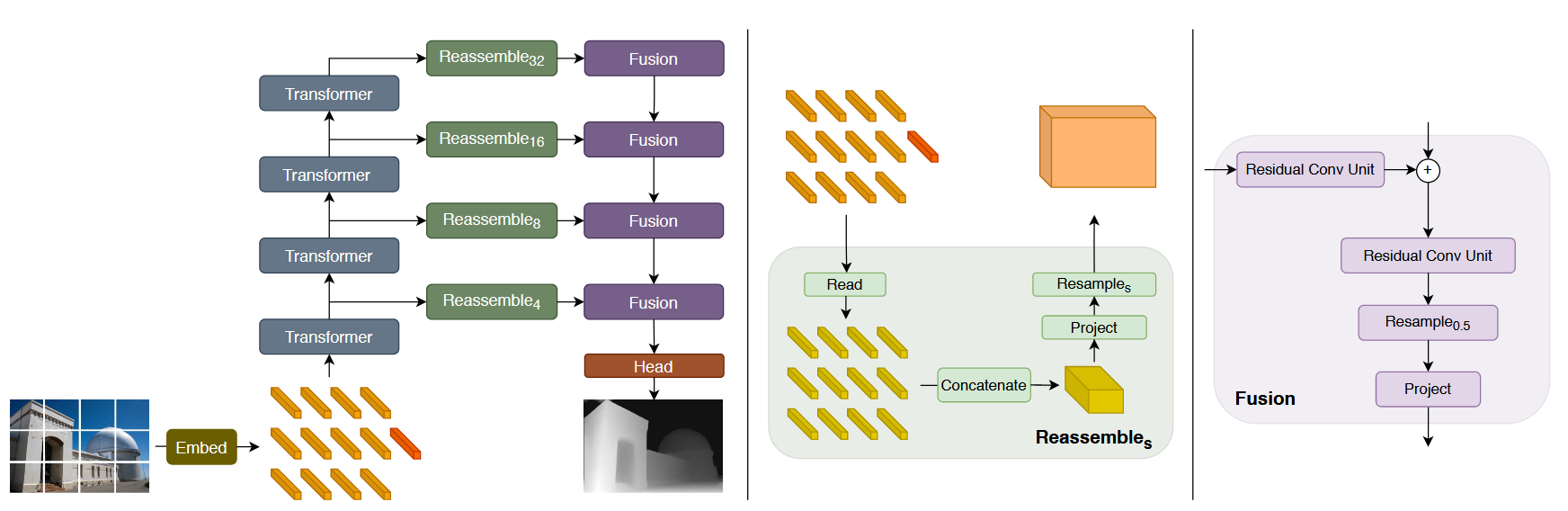
Transformer Encoder
Embedding Method
- Directly flatten the patches into vectors and individually embedded using linear projection
- Alternatively, apply ResNet to the patches and uses the pixel features of the resulting feature maps as tokens
Readout Token
Following work in NLP (such as BERT), the vision transformer additionally adds a special token that is not grounded in the input image and serves as the final, global image representation which is used for classification. We refer to this special token as the readout token
Convolutional Decoder
In the decoder module, we propose a simple three-stage Reassemble operation to recover image-like representation from the output tokens of arbitrary layers of the transformer encoder
Read
First map the token to a set of tokens that is amenable to spatial concatenation into an image-like representation.
During this process, the readout token can be either ignored or added to the output tokens
Concatenate
Reshape the tokens into an image-like representation by placing each token according to the position of the initial patch in the image
Resample
Finally pass this representation to a spatial resampling layer that scales the representation to size with features per pixel
by upsampling convolutional layers
Handling varying image sizes
As long as the image size is divisible by , the embedding procedure can be applied and will produce a varying number of image tokens